5
Social Indicators
Training
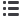
Severity Rate of Workplace Accidents (with Work Days Lost)
In 2014 the severity rate of workplace accidents (with lost work time) in
the group was slightly up.
Similarly to the previous indicator, a slight difference in absolute data in
the smaller structures can lead to a significant variation in relative values.
Severity Rate of Workplace Accidents (with Work Days Lost)
GRI
UNGC
OECD
G4-LA6
1
V
2014
2013
C+G
0.12
0.11
UMG
0.07
0.05
Vivendi Village
0.02
-
Corporate
-
-
Sub-total
0.09
0.07
GVT
0.18
0.14
Total
0.14
0.11
Calculation
method:
Number of days lost due to workplace accidents × 1,000
Average annual headcount × annual hours worked
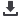
Occupational Illnesses
*
In France, occupational illnesses are those officially reported and
recognized by the French Social Security scheme. In other countries,
occupational illnesses are defined in accordance with local laws or, if
no such local laws exist, by the International Labor Organization (ILO)
(1)
.
On the whole, the group’s businesses have little exposure to occupational
illnesses.
Occupational Illnesses
GRI
UNGC
OECD
G4-LA6
1
V
2014
2013
Consolidated data
(a)
30
(a)
19
*
This data includes GVT.
(a)
Brazilian legislation gives a broad interpretation of this concept,
which explains almost this entire figure in 2014 and the entire
figure in 2013. Moreover, a change in the reporting of occupational
illnesses was made between 2013 and 2014.
(1)
For a complete list of these diseases see the ILO website.
5.5. Training
■
■
5.5.1. Training Policies of the Business Units
Each of the group’s major subsidiaries implements a vocational training
policy suited to the requirements of its businesses and the rapid changes
experienced by them, making skills development a major component of
its HR policy.
p
p
Canal+ Group gives priority to collective initiatives to meet business
challenges as quickly and as efficiently as possible.
Its training teams have developed a new program, EXPERT+, to
strengthen the business segment expertise of employees through
specific models (such as “Media and Digital Marketing,” “From Belief
to Measurement,” and “From Analysis to Recommendation”).
Special emphasis has also been placed on digital through three inter-
company themes:
–– sharing a minimum knowledge base (including familiarity with the
players, the new digital economic models and the revolution in
uses),
–– putting new tools into practice (such as web analytics), and
–– supporting business transformation (including written and oral
versatility in the Call Centers and working with trendsetters).
Training tools have been developed for managers. These are aimed
at helping every employee to develop his or her skills so that they can
attain their highest potential.
p
p
At UMG, training methods are often individualized in such a way that
the bulk of training is done gradually and in work situations. This
means that substantial numbers of training hours are not recorded.
Therefore, an assessment of the number of hours of training does
not reflect the reality of the training efforts actually undertaken by
the music companies. In 2014, training sessions were introduced
on, among other topics, competition and monopolies (UMG China),
intensive English (UMG Poland), marketing trends reflected in the
social media, big data and visual technology (UMG South Korea). In
addition, a dedicated international training team was established.
p
p
At GVT, training is done on-site or remotely, using a modular approach
and e-learning methods. It has three focuses: training in the skills
needed in the different business lines, perfecting skills, and personal
growth programs.
42
Non-Financial Indicators Handbook 2014